Bariatric surgery
What is Roux-en-Y gastric bypass?
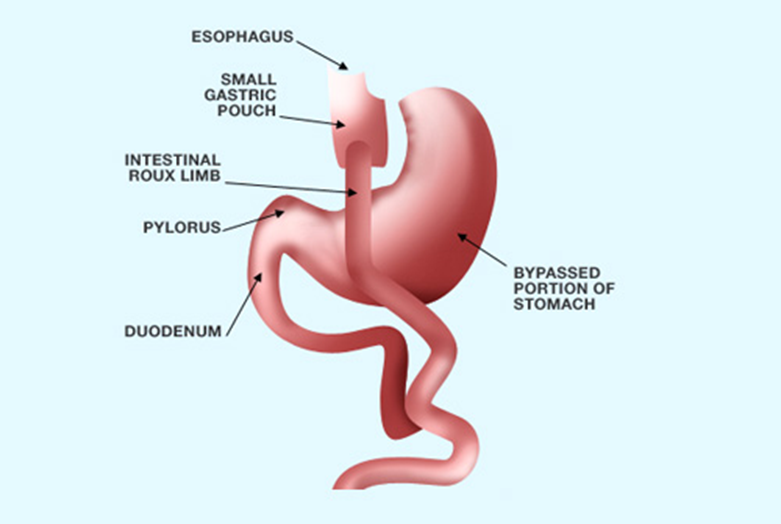
Gastric bypass restricts food intake and the amount of calories and nutrients the body absorbs. In addition to creating a smaller stomach pouch, the surgery changes the body's normal digestive process. As a result, food bypasses a large part of the stomach and most of the small intestine.
Gastric bypass surgery can be performed through an open procedure or a laparoscopic (minimally invasive) procedure. Laparoscopic surgery is performed using small incisions — and usually means a shorter hospital stay, faster recovery, smaller scars, and less pain than open surgical procedures. Most surgeons prefer the laparoscopic approach.
During a gastric bypass procedure the surgeon first creates a small stomach pouch and then attaches a section of the small intestine directly to the pouch. This allows food to bypass a portion of the small intestine, which absorbs calories and nutrients. Having a smaller stomach pouch causes you to feel full sooner and eat less food; bypassing a portion of the small intestine means your body absorbs fewer calories. Gastric bypass patients report an early sense of fullness and satisfaction that reduces the desire to eat.
Additional Resource
Questions?
If you can't find an answer, please feel free to contact our Customer Service Customer Service Customer Service
Questions?
If you can't find an answer, please feel free to contact our Customer Service
Employer web tools
Benefit Tracker
Check benefits, eligibility, incentive and utilization
Rate finder is now in the Producer Dashboard
Log in with your current username and password to create quotes for groups up to 50.
Producer DashboardLog in






Hello.
We have exciting news to share. ODS is changing its name to Moda Health.
Moda comes from the latin term "modus" and means "a way". We picked it because that's what we are here to do: help our communities find a way to better health.
Together, we can be more, be better.
Please select the state you live in, or the state where your employer is headquartered, so we can tailor your experience:

Hello.
Please select the state you live in, or the state where your employer is headquartered, so we can tailor your experience:
Privacy notice
We use cookies and similar analytics technologies to understand how visitors interact with our website, improve performance, and enhance user experience. These tools help us analyze traffic patterns and usage trends.
We do not collect or store personal information, track users for advertising purposes, or use social media plugins.
By continuing to use this site, you acknowledge our use of cookies for analytics purposes only. For more information, please refer to our Privacy Policy.
Changing your location to Oregon
You can return to your previous location in the site header.


